
1. Acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-isopropanol are not the residues of BIPB or DCP decomposition, but substances generated during the decomposition process.

The molecular structure and decomposition products of the crosslinking agent DCP.
At present, some foaming products in the European Union have begun to ban the use of DCP. Usually, the substances produced by the decomposition of the crosslinking agent when it acts on the crosslinking agent (theoretically) are: methane, acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol (2-phenylisopropanol). Among them, acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol have a relatively strong odor.
The molecular structure of DCP is as follows:

After the two benzene rings in the above structure are cracked, they are combined to form new benzene ring-containing compounds, including acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol, which account for the majority.
As shown in the figure below: the structure on the right is formed from the left. It is acetophenone.

As shown in the figure below: The structure on the right is formed from the left. It is 2-phenyl-2-isopropanol.
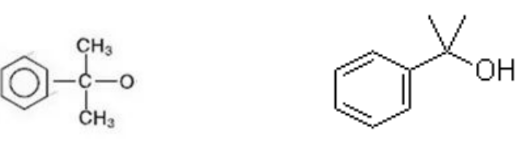
2.Why the Acetophenone/2-Phenyl-2-Proplanol content in the finished product exceeds the standard
Under the EU ban, it was originally thought that if DCP was not used and BIPB was used instead, there would be no acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol, but in fact the test results still showed that there were acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol. Let’s take a look at the molecular structure of the odorless bridging agent in the figure below and compare it with the molecular structure of DCP above.

In addition to the lack of a benzene ring, the other groups are also different, that is to say, there will be some similar substances in the composition after the decomposition and release of active oxygen. The theoretical decomposition products are:
acetone,
methane,
dihydroxydiisopropylbenzene,
tert-butyl alcohol,
diacetylphenoxide,
acetyl-2-hydroxyisopropylbenzene.
Especially benzene compounds. Therefore, it is understandable that there are still certain PPM attempts to test acetophenone and 2-phenyl-2-propanol.
Acetophenone is also called acetophenone, and diacetylphenoxide may also exist as a form of acetophenone.
From the molecular structure of acetophenone:

The molecular structure of BIPB is shown below

If under certain conditions the molecular bonds are broken and the following structure remains:

It is very likely that when one empty bond of carbon is connected to oxygen and the other empty bond is connected to a hydrogen, acetophenone (acetophenone) on the right is formed, and the principle is similar to the formation of formamide.
The structural formula of 2-phenyl-2-propanol is as shown below: When BIPB decomposes, the molecules break apart to form the structure on the left below.
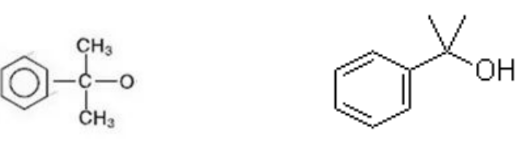
We know that the function of active oxygen after disconnection is to extract hydrogen, thus forming the 2-phenyl-2-propanol pathway on the right.
Siperox® BIBP 40%
Siperox® BIBP 96%
Contact Us Now!
If you would like more information about 1,3-Bis(1-tert-butylperoxy-1-methylethyl)benzene or would like to request samples, please send an e-mail to info@sinocurechem.com or use the website’s live chat facility for a prompt response.
